Connect your device to the largest mobile network in Australia with M2M One. We stock a variety of form factors: Standard, Micro, Nano, Industrial and Machine Solderable.

Connectivity helping businesses grow across Australia and New Zealand
850,000
99.3
35
Trusted by thousands across Australia & New Zealand
Connect in 3 simple steps
1. Book a free meeting
Fill out a basic form for an obligation-free meeting at a time that suits.
2. Select a plan
Select one of our affordable and flexible solutions to suit your business.
3. Connect your devices
Sit back and relax as our team connects and manages your IoT devices.
Find the perfect solution for you
Two different solutions, created to service your unique situation
For Small Deployments
Simple IoT Connection
Our simple IoT connection service provides a straightforward and efficient solution for connecting your devices to the internet quickly and reliably, ideal for businesses seeking a simple, no-fuss activation of the IoT devices.
- 72 Hours Delivery
- Cost-Effective
- Flexibility
For Large Deployments
Ongoing IoT Management
M2MOne’s Complete Managed Services take the complexity out of IoT deployments with end-to-end management. This comprehensive service includes initial setup and activation, to ongoing monitoring and support.
- Full Lifecycle Management
- Enhanced Security
- Dedicated Support
Standard SIM Cards

M2M Standard SIM Card
The standard SIM card, also known as a “mini SIM,” was the first SIM card’s size iteration and is larger than the subsequent micro and nano versions.
Form Factor: 2FF
Dimensions: 25mm x 15mm
Environment: Normal Conditions
Operational Temperature: -25°C to +85°C
Anti-Corrosion: N/A
Endurance: Average 500,000 write/erase cycles
Data Retention Time: Average 5 to 7 years based on typical usage
Flash Memory: 64KB
Vibration Standard: N/A
Package: Plug-In Card (uses SIM tray or holder)
Typical Application: Most M2M applications, including Vehicle Tracking, Vending Machines, Payments & Signage.
M2M Micro SIM Card
Micro SIM cards are a smaller version of standard SIM cards. They were introduced to accommodate the design of smaller and slimmer devices. The micro SIM carries the same information as the standard SIM, such as the subscriber’s identification details, but it’s physically smaller in size.
Form Factor: 3FF
Dimensions: 15mm x 12mm
Environment: Normal Conditions
Operational Temperature: -25°C to +85°C
Anti-Corrosion: N/A
Endurance: Average 500,000 write/erase cycles
Data Retention Time: Average 5 to 7 years based on typical usage
Flash Memory: 64KB
Vibration Standard: N/A
Package: Plug-In Card (uses SIM tray or holder)
Typical Application: Small form factor M2M applications, including mHealth, GPS, Tablets & Dispatch Units.

M2M Nano SIM Card
The nano SIM card is the smallest of the three types. The reduction in size was a further adaptation to the ever-shrinking dimensions of modern mobile devices.
Form Factor: 4FF
Dimensions: 12.3mm x 8.8mm
Environment: Normal Conditions
Operational Temperature: -25°C to +85°C
Anti-Corrosion: N/A
Endurance: Average 500,000 write/erase cycles
Data Retention Time: Average 5 to 7 years based on typical usage
Flash Memory: 64KB
Vibration Standard: N/A
Package: Plug-In Card (uses SIM tray or holder)
Typical Application: Smallest form factor M2M applications, including Tablets, Mobile Payment & Terminals.
Specialist SIM Cards
M2M Industrial Strength SIM Card
Form Factor: Ruggedised 2FF or 3FF
Dimensions: 25mm x 15mm
Environment: Extreme conditions of temperature and vibration
Operational Temperature: -40°C to +105°C
Anti-Corrosion: Yes
Endurance: Average 500,000 write/erase cycles
Data Retention Time: Average 10 years based on typical usage
Flash Memory: 64KB
Vibration Standard: Complies to ETSI TS 102.671 – Vibration VA automotive standard
Package: Plug-In Card (uses SIM tray or holder)
Typical Application: Industrial M2M applications, including smart metering, mining, vehicle telematics and environmental monitoring
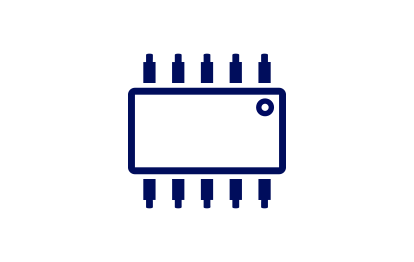
M2M Surface Mounted/
Solderable SIM Chip
Form Factor: MFF2
Dimensions: 6mm x 5mm
Environment: Extreme conditions of temperature and vibration
Operational Temperature: -40°C to +105°C
Anti-Corrosion: Yes
Endurance: Average 500,000 write/erase cycles
Data Retention Time: Average 10 years based on typical usage
Flash Memory: 64KB
Vibration Standard: Complies to ETSI TS 102.671 – Vibration VA automotive standard
Package: SON8/VQFN8 packaging for automated assembly
Typical Application: Industrial M2M applications, including smart metering, mining, vehicle telematics and environmental monitoring
Step into the future with M2M One
The complex world of IoT is made simpler when you have the right tools and allies. For both seasoned tech experts and businesses beginning their IoT journey, understanding and leveraging M2M SIM cards is essential. While many may have questions about implementation and scalability, rest easy knowing Telstra’s global M2M IoT SIM cards provide scalability that aligns with your growth. For niche applications, explore our advanced NB-IoT solutions, or consider our specialised SIMs designed specifically for lifts. To ensure uninterrupted connections, our managed failover service is unparalleled, and for heightened security, our M2M VPN services are top-tier.
Frequently asked questions
What is an M2M SIM card?
An IoT SIM card is a type of Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) specifically designed for use in Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Unlike traditional SIM cards primarily used in mobile phones for voice communication and data services, IoT SIM cards provide cellular connectivity for IoT devices, enabling them to send and receive data over mobile networks.
What is the difference between M2M and standard SIM cards?
IoT SIM cards and normal SIM cards are designed for fundamentally different purposes, reflecting the distinct requirements of IoT devices versus consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets. While IoT SIM cards are engineered to facilitate low power consumption, extended operational longevity, and wide-ranging connectivity for devices scattered across various environments, normal SIM cards focus on providing high-speed data and voice services for daily consumer use. The key distinctions are as follows;
- Network and Data Priorities: IoT SIM cards support low-power, long-range technologies such as LTE-M and NB-IoT, optimising for minimal data exchange and prolonged battery life. In contrast, normal SIM cards are geared towards high bandwidth and data rates to accommodate streaming, browsing, and downloading.
- Power Consumption and Longevity: IoT SIM cards are designed with low-power protocols to extend device battery life, often necessary for years of operation without maintenance, unlike normal SIM cards, which are used in devices with more frequent charging cycles.
- Roaming and Coverage: IoT SIM cards typically offer global coverage with the ability to switch between networks for optimal connectivity, essential for mobile or international IoT deployments. Normal SIM cards, however, usually restrict users to a single network provider and may incur additional costs for international roaming.
What is the benefit of an M2M SIM?
- Wide Coverage: IoT SIM cards often come with agreements that allow them to operate across multiple networks and in various countries, providing broader coverage than standard SIMs. This feature is crucial for IoT applications that require mobility or are deployed in remote areas.
- Longevity: IoT devices are typically deployed in the field for extended periods, so IoT SIM cards are designed to have a longer lifespan than traditional SIM cards.
- Low Power Consumption: Many IoT devices rely on battery power and operate in power-saving modes. IoT SIM cards support low power consumption protocols such as LTE-M and NB-IoT, which are optimised for IoT applications requiring low data rates and long battery life.
- Small Form Factors: IoT SIM cards are available in various form factors, including embedded SIMs (eSIMs), which are soldered directly onto the device’s circuit board. This makes them suitable for a wide range of IoT devices, from small sensors to large industrial machines.
- Security: Security is a critical concern for IoT devices. IoT SIM cards often include advanced security features to protect the data being transmitted and ensure the integrity of the device’s connectivity.
- Scalability and Management: IoT SIM cards can be managed remotely through platforms that allow users to activate, deactivate, and monitor their SIMs across thousands or even millions of devices. This capability is essential for managing large-scale IoT deployments.
Do I need a SIM card for IoT?
Whether you need a SIM card for your IoT (Internet of Things) device depends on several factors, including the type of connectivity required, the deployment environment, and the specific use case of the device. Here’s a breakdown of considerations to help you determine if an IoT SIM card is necessary for your project:
- Type of Connectivity Required
- Cellular Connectivity: If your IoT device needs to transmit data over long distances or in areas without WiFi or other types of networks, a SIM card is essential for cellular connectivity. Cellular networks offer wide coverage, making them ideal for mobile devices or remote monitoring applications.
- Local Network Connectivity: For devices that operate within a localised area, such as a smart home or office environment, and can reliably use WiFi, Bluetooth, or other short-range communication technologies, a SIM card may not be necessary.
- Deployment Environment
- Remote or Mobile Environments: Devices deployed in remote locations (e.g., agricultural sensors, wildlife tracking) or those that are mobile (e.g. logistics and fleet management) often require a SIM card for cellular connectivity to ensure they can transmit data back to the central system regardless of their location.
- Controlled Environments: In controlled environments with stable access to WiFi or LAN connections (e.g., industrial automation within a factory, smart buildings), devices might not need a SIM card for connectivity.
- Specific Use Case
- Global Deployment: If the IoT device is intended for use in multiple countries or needs to switch networks seamlessly, an IoT SIM card that supports global connectivity can simplify deployment and operation.
- Critical Operations: For critical applications where reliable connectivity is paramount (e.g., health monitoring, emergency response systems), the redundancy provided by a cellular connection via a SIM card can be a crucial backup to other forms of connectivity.
- Cost and Data Requirements
- Data Plan Costs: Consider the costs associated with cellular data plans. For devices that transmit small amounts of data infrequently, the cost may be minimal. However, for devices that require constant connectivity and transmit large amounts of data, the costs can be significant.
- Data Volume and Speed: Evaluate the data volume and speed requirements of your IoT application. SIM cards and cellular networks can accommodate a wide range of needs, from low-power, narrowband applications to high-speed, data-intensive applications.
What is the difference between M2M and IoT?
| M2M (Machine-to-Machine) | IoT (Internet of Things) | |
| Definition | Direct and automated communication between two machines or devices, often for specific and isolated functions | A comprehensive ecosystem of interconnected devices and sensors that communicate over the internet, enabling data collection, analysis, and an integrated response across a wide range of applications. |
| Scope and Interaction | Limited to specific, standalone tasks within closed systems. | Encompasses a wide ecosystem integrating diverse devices and systems for complex interactions and data exchange. |
| Connectivity | Primarily relies on cellular or wired networks for point-to-point communication. | Utilises a wide range of technologies (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, LoRaWAN, Zigbee, etc.) for internet-based communication and interaction. |
| Application Areas | Focused on industrial and enterprise settings for tasks like remote monitoring, control systems, and telemetry. | Expansive across multiple sectors including smart homes, healthcare, agriculture, smart cities, and industrial automation, with applications that integrate devices for smarter outcomes. |
| Interoperability | Typically lower, with systems often designed for isolated operations using proprietary protocols. | Emphasises high interoperability and standardisation, facilitating seamless interaction among diverse systems and platforms. |
What network does M2M use?
M2M operates on multiple networks, depending on the provider and region. With Telstra IoT SIMs, you’ll benefit from Australia and New Zealand’s most extensive mobile network, ensuring unmatched coverage.
Does M2M require internet connection?
Not always. While many M2M applications benefit from internet connectivity, some can function on direct device-to-device communications, depending on the specific use case.

